The Shift from SEO to GEO: What You Need to Know
Why traditional search engine optimization techniques are failing in the age of generative AI, and how to adapt.
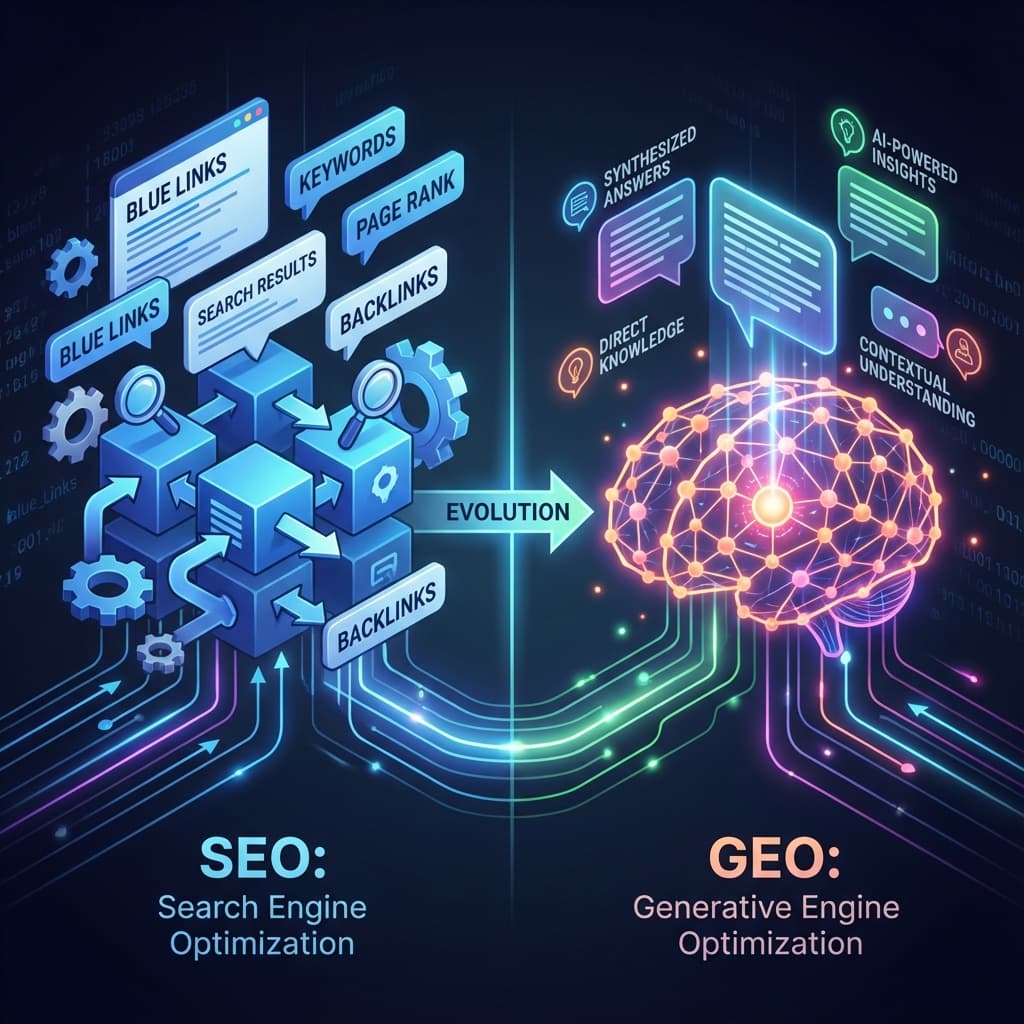
The Shift from SEO to GEO
The landscape of search is undergoing a seismic shift. For two decades, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has been the gold standard for digital visibility. Marketers and developers alike honed their skills in keyword research, backlink building, and technical optimization to rank higher on a list of blue links.
The Rise of Generative Engines
Today, users aren't just searching; they're conversing. Platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity don't just index the web—they read it, understand it, and synthesize answers. This has gave birth to a new discipline: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
Key Differences
| Feature | SEO | GEO | | :--- | :--- | :--- | | Goal | Rank #1 on a SERP | Be the cited source in an answer | | Target | Crawlers & Indexers | Large Language Models (LLMs) | | Content | Keyword-dense | Entity-rich & Authoritative | | Metrics | CTR & Rankings | Share of Voice & Sentiment |
Adapting Your Strategy
To succeed in this new era, brands must pivot from "optimizing for clicks" to " optimizing for comprehension." This means:
- Structuring Data: Using JSON-LD and semantic HTML to help LLMs understand the relationships between entities on your site.
- Building Authority: LLMs prioritize information from credible, high-E-E-A-T sources to minimize hallucinations.
- Direct Answers: Formatting content to directly answer user questions, increasing the likelihood of being picked up as a snippet or citation.
Stratos helps you navigate this transition by providing the analytics and insights needed to measure your performance in the generative web.
Share this article